The following mass extinction may be pushed by excessive warmth—and people may very well be among the many casualties.
Supercomputer local weather fashions have discovered that within the subsequent 250 million years, practically all mammals could turn out to be extinct because the planet heats to unsurvivable ranges, exacerbated by a brand new supercontinent forecast to type close to the equator, in response to a brand new examine revealed within the journal Nature Geoscience.
People are additionally within the firing line of extinction on this state of affairs. Nonetheless, we’re extra probably than different species to outlive as a result of our technological developments.
Picture by PATRICK T. FALLON/AFP through Getty Photos
“If we solely have a look at people’ pure means to outlive excessive warmth (no expertise allowed) then there are a number of warmth stress thresholds that may’t be crossed typically,” Alexander Farnsworth, lead writer of the paper and senior analysis affiliate on the College of Bristol within the U.Ok., advised Newsweek.
“Publicity to wet-bulb temperatures (which considers warmth and moisture) above 35 levels C [95 degrees F]. (this may very well be decrease at 32 levels C [89.6 F] latest analysis has steered) for over six hours could be deadly (this even considers complete inactivity, full shade, absence of clothes, and limitless ingesting water). Likewise, dry-bulb temperatures (what you measure of a thermometer) above 40 levels C [104 F]. and low humidity for a sustained time frame can be deadly.”
“If we consider expertise, we will survive due to constructing environmentally managed shelters with air con. However we might probably must construct different services to deal with meals manufacturing as nicely,” he mentioned.
College of Bristol
These intense temperature extremes—presumably between 104 to 158 levels F—are predicted to happen as a result of elevated carbon dioxide within the environment, largely on account of tectonic exercise triggering volcanic eruptions, in addition to because of the solar itself producing about 2.5 p.c extra radiation.
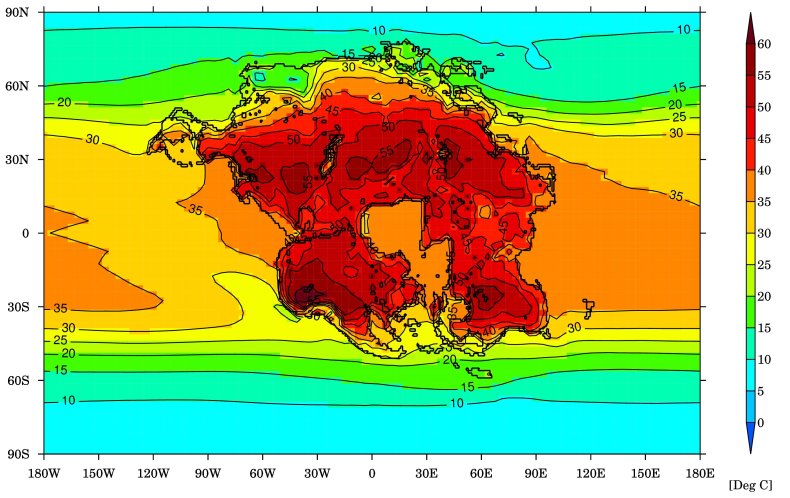
“In our examine we present that international temperatures may very well be round 10-15 levels Celsius [18-27 F] hotter than at the moment and on simply the land itself, it may very well be between 25-30 levels Celsius [45-54 F] hotter on common than at the moment,” Farnsworth mentioned.
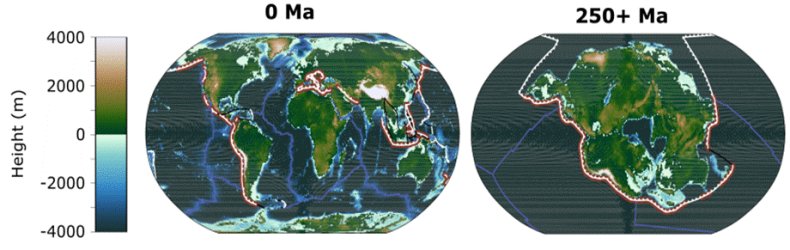
The authors predict that this warmth concern will turn out to be a significant drawback as soon as the subsequent supercontinent— Pangea Ultima— varieties. Between 8 and 16 p.c of land shall be liveable for mammals. It’s because the continent shall be located across the equator of the Earth, the place the climate is hottest, in addition to the CO2 thrown out by tectonic exercise because of the shifting continents.
“We present that there are three major components that drive to an excessive local weather state that may render the Earth in 250 million years inhospitable. [Firstly,] with out altering carbon dioxide concentrations within the environment (saved at ranges earlier than the economic revolution) and the solar’s brightness (i.e. the quantity of power the solar emits) additionally at present-day ranges and solely altering the place the continents and re-arranging them right into a supercontinent we present that this alone raises land floor temperatures considerably, primarily as a result of a lot of the land floor being within the tropics now,” Farnsworth explains.
“The solar is round 2.5 p.c brighter in 250 million years, including extra power incident to the Earth additional warming the world. [Additionally,] the tectonic assemblage of this supercontinent creates extra volcanic degassing that’s emitted to the environment (we predict round 600 ppm CO2 being the likeliest).”
College of Bristol
Mammals are notably at risk from these temperature will increase, as we now have advanced to face up to colder temperatures a lot better than we will deal with hotter temperatures. Based on the examine, mammals have decreased our decrease temperature restrict over time, however our higher restrict has stayed pretty fixed, placing us vulnerable to hotter temperature extremes.
“As mammals generate their very own physique temperatures that are typically fixed by thermoregulation, for example for people that is typically round 37 C [98.6 F]. When it will get scorching we calm down by sweating. That is the physique’s response to the physique overheating to dissipate the warmth. To ensure that the warmth dissipation course of to work, the encompassing air should be cooler than the pores and skin, which should be cooler than the core physique temperature,” Farnsworth mentioned.
“The cooler pores and skin is then in a position to take up extra warmth from the core and launch it into the atmosphere. If the temperature is hotter than the temperature of the pores and skin, metabolic warmth can’t be simply launched and probably harmful overheating can ensue relying on the magnitude and period of the warmth stress. Over sustained intervals this overheating can result in heatstroke that may trigger mind tissue or different very important organs to swell, leading to everlasting harm.”
Moreover, excessive warmth will destroy the habitat that many mammals depend on, together with our meals sources.

Picture by Christopher Furlong/Getty Photos
“Vegetation, typically, don’t like temperatures above 40 (there are some exceptions to this), sadly, a lot of the continent might expertise temperatures in extra of this. Vegetation underpin the meals pyramid, for those who begin to take away them over huge areas you stress the remainder of the species (e.g. bugs) who depend on them and subsequently the upper trophic stage species that in flip depend on them as a meals supply.”
It will probably affect numerous different courses of animals, however this examine targeted on mammals particularly.
“It’s onerous to say in regards to the different species as we did not give attention to them on this examine. Nonetheless, what will be mentioned is that this is able to not be a really hospitable world for a lot of of them both.”
Do you could have a tip on a science story that Newsweek ought to be masking? Do you could have a query about excessive warmth? Tell us through science@newsweek.com.




